Understanding Large Language Models¶
约 335 个字 4 张图片 预计阅读时间 1 分钟
Goal
understanding LLMs by implementing a ChatGPT-like LLM based on the transformer architecture.
What is an LLM?¶
An LLM is a neural network designed to understand, generate, and respond to human-like text.
Stages of building and using LLMs¶
- When it comes to modeling performance, custom-built LLMs (those tailored for specific tasks or domains) can outperform general-purpose LLMs.
- The general process of creating LLM includes pretraining and finetuning.
- pretraining: the initial phase where a model like an LLM is trained on a large diverse dataset to develop a broad understanding of language.
- finetuning: the pretrained model serve as a foundational resource that can be further refined. finetuning is a process where the model is specifically trained on a narrower dataset that is more specific to particular tasks.
Transformer architecture¶
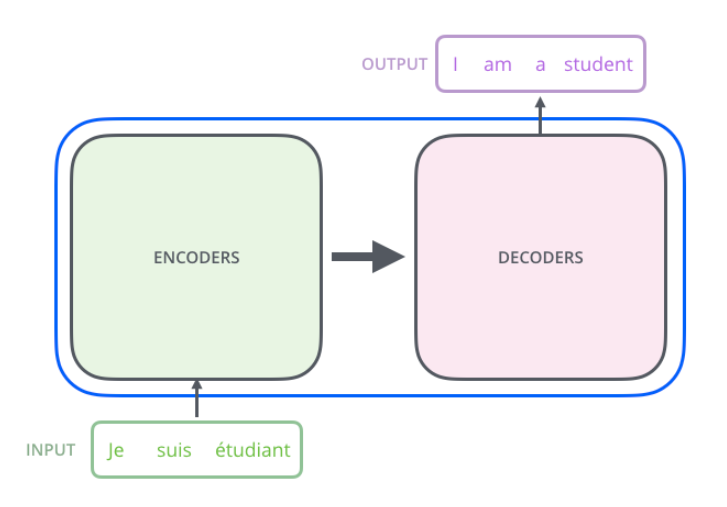
- The encoder module processes the input text and encodes it into a series of numerical representations or vectors that capture the contextual information of the input.
- The decoder module takes these encoded vectors and generates the output text from them.
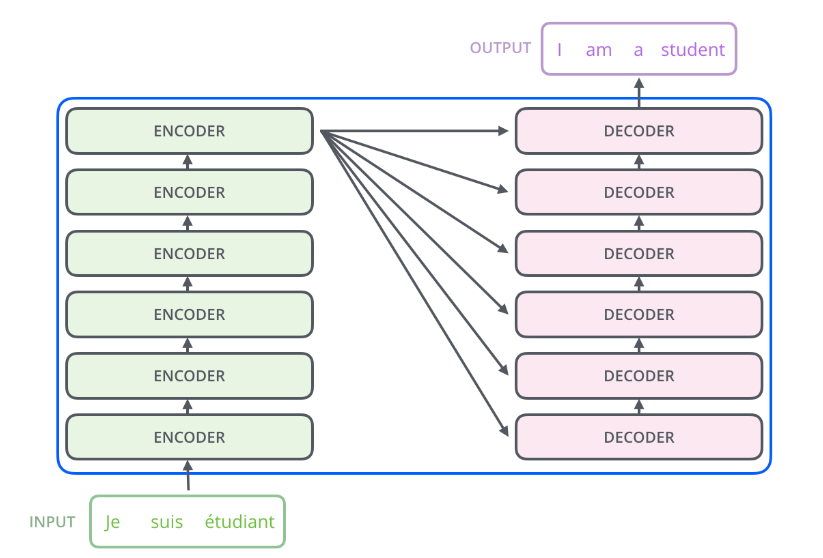
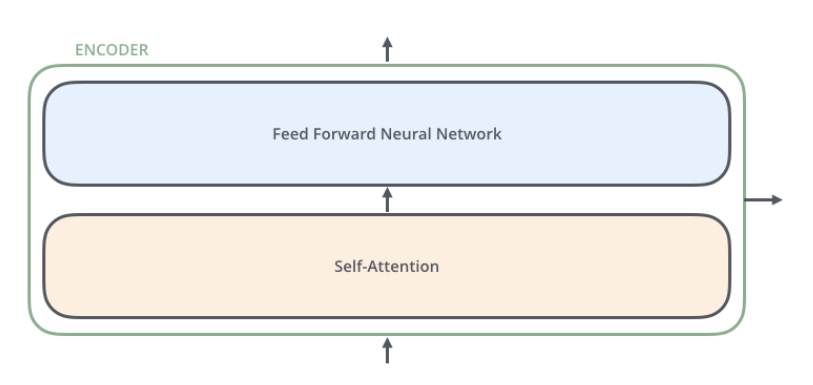
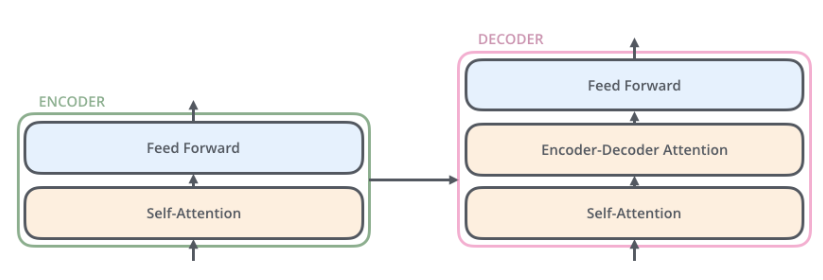
- Both the encoder and decoder consist of many layers connected by a self-attention mechanism, which allows the model to weigh the importance of different words or tokens in a sequence relative to each other.enable the model to capture long-range dependencies and contextual relationships within input data
Bert¶
BERT and its variants specialize in masked word prediction, where the model predicts masked or hidden words in a given sentence.
GPT¶
GPT focus on the decoder portion of the original transformer architecture and is designed for tasks that require generating texts.
GPT models are adept at executing both zero-shot and few-shot learning tasks:
- Zero-shot learning: the ability to generalize to completely unseen tasks without any prior specific examples.
- few-shot learning: learning from a minimal number of examples the user provides
Utilizing large datasets¶
token
- a unit of text that a model reads
- the number of tokesn in a dataset is roughly equivalent to the number of words and punctuation characters in the text.
最后更新:
2024年7月26日 16:12:06
创建日期: 2024年7月24日 22:50:37
创建日期: 2024年7月24日 22:50:37